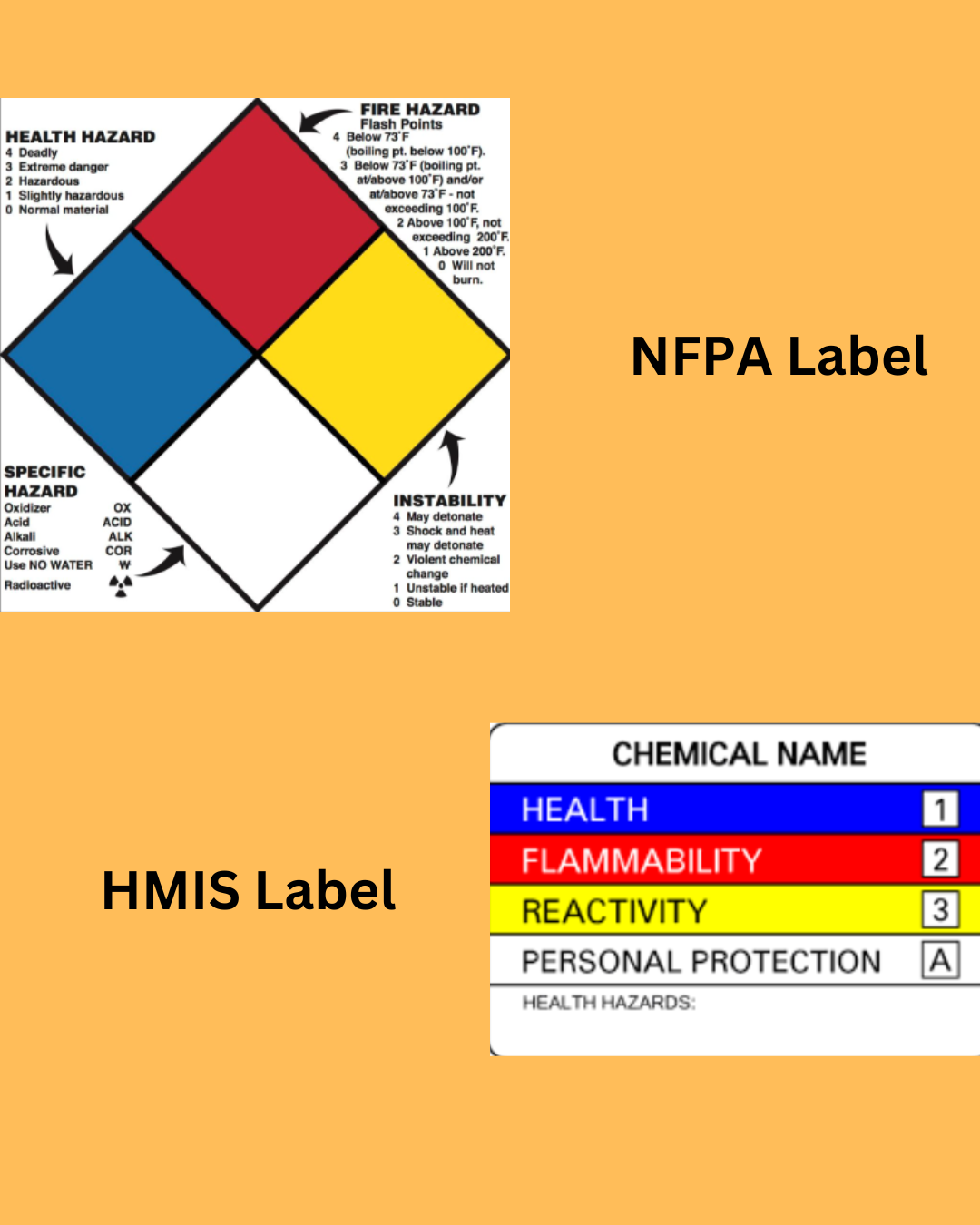
In industrial and workplace environments, hazardous materials pose significant risks if not handled properly. To ensure safety, organizations rely on standardized labeling systems like the Hazardous Materials Identification System (HMIS) and the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) labels. These labels provide crucial information about chemical hazards, helping workers take necessary precautions.
What is the Hazardous Materials Identification System (HMIS)?
The HMIS labeling system was developed by the American Coatings Association (ACA) to help employees identify and handle hazardous substances safely. It provides a structured format for categorizing chemical hazards and recommending protective measures. The HMIS label consists of a color-coded bar with numerical ratings that indicate the severity of different hazards:
HMIS Label Breakdown
- Blue (Health Hazard):
- 0: No significant risk to health.
- 1: Slight irritation or minor reversible injury.
- 2: Temporary or moderate health effects, requiring first aid.
- 3: Serious injury risk even with short exposure.
- 4: Severe or life-threatening hazard.
- Red (Flammability Hazard):
- 0: Will not burn under normal conditions.
- 1: Slightly combustible.
- 2: Moderately flammable.
- 3: Easily ignitable.
- 4: Extremely flammable.
- Orange/Yellow (Physical Hazard):
- 0: Stable, no reactivity concerns.
- 1: May become unstable at high temperatures or pressure.
- 2: Capable of violent reactions under specific conditions.
- 3: Explosive potential under normal conditions.
- 4: May detonate or explode.
- White (Personal Protection):
- This section uses letters or symbols to recommend personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gloves, masks, face shields, or respirators.
Benefits of HMIS
- Standardized method for identifying workplace chemical hazards.
- Helps employees quickly understand the risks of chemicals.
- Ensures compliance with OSHA’s Hazard Communication Standard (HCS).
- Reduces workplace injuries by guiding safe chemical handling and PPE usage.
What is the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) Label?
The NFPA label, commonly referred to as the NFPA 704 Diamond, is a standardized system used primarily by emergency responders and fire safety professionals. It provides a quick, visual reference for understanding a material’s hazards at a glance.
NFPA Label Breakdown
The NFPA diamond consists of four color-coded sections, each representing a different type of hazard:
- Blue (Health Hazard): Assesses toxicity and health risks on a 0-4 scale:
- 0: No hazard.
- 1: Mild irritation or minor effects.
- 2: Temporary incapacitation or residual injury.
- 3: Severe or permanent health effects.
- 4: Deadly with short exposure.
- Red (Flammability Hazard): Indicates flammability level on a 0-4 scale:
- 0: Will not burn.
- 1: Must be preheated before ignition.
- 2: Ignites under moderate heat.
- 3: Ignites easily at room temperature.
- 4: Extremely flammable.
- Yellow (Instability/Reactivity Hazard): Shows the potential for dangerous reactions:
- 0: Stable.
- 1: Normally stable but may react under specific conditions.
- 2: Unstable with violent chemical changes.
- 3: Can detonate with shock or heat.
- 4: May detonate or explode.
- White (Special Hazard Information): Contains symbols for specific hazards such as:
- OX (Oxidizer): Can intensify fires.
- ACID: Corrosive acid.
- ALK: Corrosive base/alkali.
- W (Water Reactive): Reacts dangerously with water.
- Radiation symbol: Indicates radioactive materials.
Key Uses of NFPA Labels
- Provides critical hazard information for first responders during emergencies.
- Helps fire departments assess risks before engaging in firefighting.
- Assists facilities in compliance with fire safety and hazardous material storage regulations.
Differences Between HMIS and NFPA Labels
| Feature | HMIS | NFPA |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Workplace safety & PPE guidance | Emergency response & fire safety |
| Health Rating | Blue bar with 0-4 scale | Blue section with 0-4 scale |
| Flammability | Red bar with 0-4 scale | Red section with 0-4 scale |
| Reactivity | Orange/yellow bar with 0-4 scale | Yellow section with 0-4 scale |
| PPE Guidance | White section (letters/symbols) | Not included |
Importance of Understanding These Labels
Understanding HMIS and NFPA labels is essential for workplace safety, fire prevention, and regulatory compliance. Employees should be trained on how to read these labels to handle hazardous materials appropriately and respond effectively in emergencies. This knowledge ensures a safer working environment by minimizing exposure to dangerous substances.
Conclusion
Both HMIS and NFPA labels play a crucial role in ensuring safety in workplaces that handle hazardous materials. While HMIS is more focused on employee safety and PPE recommendations, NFPA is designed for quick hazard identification by emergency personnel. By familiarizing yourself with these labeling systems, you can contribute to a safer working environment and improve overall hazard communication.